HashMap 源码解读
说到 HashMap,大家一定都不会陌生,不管是我们平时使用,或者是面试的时候,都会遇到它,了解其源码还是相当重要的。
HashMap 其实维护的的数据结构是 Node<K,V> 的数组加链表(下面会说到为什么),也是说的维护的 Hash 桶,什么意思呢?按照笔者个人理解就是说 HashMap 中保存数据的是一个叫 table 的数组,HashMap 有新数据时就会插入到特定生成的数组下标(如何生成下面会说到)中,如果当前下标没有数据就直接放入,只有一个数据的话,数组下标中还是会放入旧的 Node,并且将旧的 Node 作为头指针,将新的 Node 作为旧的 Node 的子节点以链表的方式保存。按照笔者个人理解,每一个数组下标可以看做是一个 Hash 桶,来放一个或多个 Node 数据。
那么 Node 是什么呢?Node 可以理解为 HashMap 中实际保存每一组 key-value 的映射项,它是实现的 Map.Entry<K,V>,下面我们来看看 Node 的源码。
1 | static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { |
Node 的源码还是一目了然了,就不用了多做解释了,再正式解读 HashMap 的主要方法之前,先看一下一些重要的参数
// 默认的容量大小 为16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
// 最大容量 2的30次方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认装载因子 为 0.75f
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// HashMap 保存数据使用的数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// HashMap 中实际保存的键值对的数量
transient int size;
// 扩容值,当 size 达到这个值时,HashMap 就要扩容
int threshold; 为 capacity * load factor
构造方法
HashMap 有四个构造方法,我们来看一下这四个方法:
1 | /** |
put 方法
上面我们看到使用了 putMapEntries 方法将原 map 放入新的 HashMap,那么它到底干了啥呢?
1 | final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) { |
上面的构造方法我们看到了会传入初始化的容量,其实这个容量并不是真正用来作为数组的容量的,而是为了来确定扩容值的,我们上面看到了的确认扩容值的方法是 tableSizeFor(initialCapacity),那么这个方法是干嘛的呢?
1 | /** |
这个方法是返回一个大于 cap 并且最接近的一个 2的n次幂的一个值来作为扩容值。
看完了构造方法,我们来看一下 HashMap 的最常用的方法,get 和 put,我们可以看到,其实 put 方法也是调用的 putVal 方法,和上面 putMapEntries 方法实际调用的是同一个方法。
1 | public V put(K key, V value) { |
所以说 put 方法就是使用的 putVal 方法:
1 | final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, |
那么是怎么往链表中放的呢?
1 | // 当这个桶里面有数据了,那就意味着要放进链表了 |
HashMap 的 put 方法就是这样的,那么 get 方法呢?在 HashMap 中的 get 方法使用的是 getNode 方法:
get 方法
1 | public V get(Object key) { |
那我们来看看 getNode:
1 | final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { |
扩容
我们看到了,上面 put 数据时会进行扩容操作,那么按道理来说 HashMap 是将 Node 数据放入到了数组下标为 (n - 1) & hash 的 Hash 桶中,当 hash 值一样时便会放入数组下标中 Node 的子节点使用链表保存,那么为什么还需要扩容呢?其实就是因为链表的长度过长时会影响我们 HashMap 的效率,所以说 HashMap 扩容就是将 HashMap 中 Hash 桶中的链表变短,而实际扩容也是这么操作的:
1 | final Node<K,V>[] resize() { |
数据迁移
我们看到了怎么更新容量和扩容值的,那么扩容完不做数据迁移,扩容又有什么意义呢?下面我们就来看看怎么做的数据迁移:
1 | ({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) |
为什么 hi 链表要放入数组的下标为 j + oldCap 中呢?这个就不得不说写这个源码的大佬的强大了,这里正好解释了上面为什么用要使用 e.hash & oldCap 来判断是插入到 lo 链表还是 hi 链表了。
我们知道,put 时是将数据放入到下标为 (n - 1) & hash 中,那么 (n - 1) & hash 是干了啥呢?我们上面说了 (n - 1) & hash 就等于 hash % (n - 1) ,其实在二进制中,取余就是取低位,这个是什么意思呢?因为 n 是2的整数次幂,这里我们整数为 m:
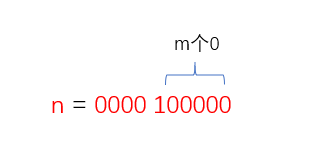
那么 n - 1 呢

都知道 0 & 任何数为0,1 & 任何数为任何数,所以 (n - 1) & hash 就是拿到了 hash 值的低 m 位,那么扩容后呢?上面说过了扩容是新的容量为旧容量的2倍,如果新容量为 n1,那么 n1 = 2*n = 2^(m+1),那么(n1 - 1) & hash 就是取 hash 值的低 m+1 位,那么新位置与旧位置差了多大呢?
通过上面的代码可以看到,距离差为 j + oldCap - j = oldCap,距离差就为 oldCap,为什么是这个呢?按照上面说的距离差应该是 (n1 - 1) & hash - (n - 1) & hash,那么就是 hash 值的后 m+1 位减去 hash 值的后 m 位,那么就等于 hash 的二进制只有第 m+1 位不确定,其它为都为 0 的值。二进制中就只有 0 和 1,如果为 0 ,那么距离差就为 0,那么就是 j 的位置,那如果 第 m+1 为 1 呢?记得上面的图吗?n 的 1 后面有 m 个 0,那么第 m+1 位为 1 那不就是 n,也就是 oldCap 吗?所以新的位置就在 j + oldCap。
那么我们怎么拿到第 m+1 位是 0 还是 1 呢?你们看 oldCap 也就是 n,只有第 m+1 位为 1 ,1 & 任何数为任何数,0 & 任何数为 0,那么第 m+1 位的值不就等于 e.hash & n,也就是 e.hash & oldCap 吗?
所以我们源码中才会判断当 e.hash & oldCap 为 0 时将节点插入到 lo 链表,不为 0 时插入到 hi 链表,我们的扩容就将一个链表巧妙的分成了两个链表。
好了,HashMap 的源码主要部分就先说到这里,如果想要一起学习的话,可以持续关注这个 GitHub项目,或者关注我的个人微信公众号。

觉得喜欢的话请给我这个 GitHub 项目 一个 Star,谢谢!